

To Book Appointment Call
Common Sports Injuries
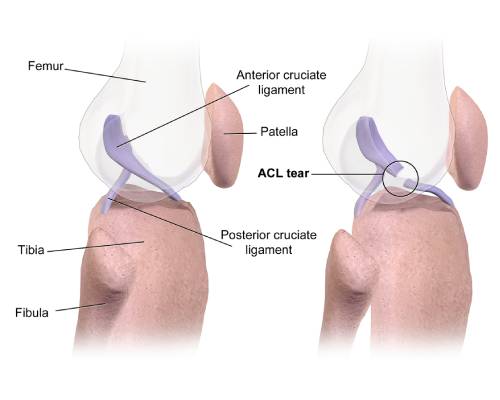
ACL Tears
- What is ACL Tear:
- An ACL (Anterior Cruciate Ligament) tear is a common knee injury, often occurring during sports activities, that involves the tearing or overstretching of the ACL.
- Causes:
- Sudden stops, twists, or impacts during sports activities. Direct blows to the knee, commonly observed in contact sports. Sudden changes in direction or pivoting.
- Symptoms:
- Audible popping sound during the injury. Immediate swelling and inflammation around the knee. Intense pain, limiting the ability to bear weight. Feeling of instability or a "giving way" sensation in the knee.
- Prevention:
- Incorporate strength training to build muscles around the knee. Focus on proper landing and cutting techniques during sports.
- Regular flexibility exercises to maintain joint mobility. Use protective gear, such as knee braces. Adhere to warm-up routines before engaging in physical activities.
- Treatment:
- Non-Surgical Approaches: RICE method (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) immediately after injury. Physical therapy to strengthen surrounding muscles and improve flexibility. Bracing for added support during recovery. Anti-inflammatory medications to manage pain and swelling.
- Surgical Intervention (ACL Reconstruction): Grafting to replace the torn ACL, often using the patient's tissue or a donor's. Arthroscopic surgery for minimally invasive reconstruction. Post-surgery, a structured rehabilitation program is crucial for optimal recovery.
- Rehabilitation:
- Gradual and supervised physical therapy. Focus on regaining full range of motion. Strengthening exercises, especially targeting the quadriceps and hamstrings. Functional exercises mimicking real-life movements. Incremental return-to-play protocols under medical guidance. Understanding the nature of an ACL tear, recognizing symptoms promptly, implementing preventive measures, and pursuing appropriate treatment options are vital steps for managing this knee injury and facilitating a successful recovery.
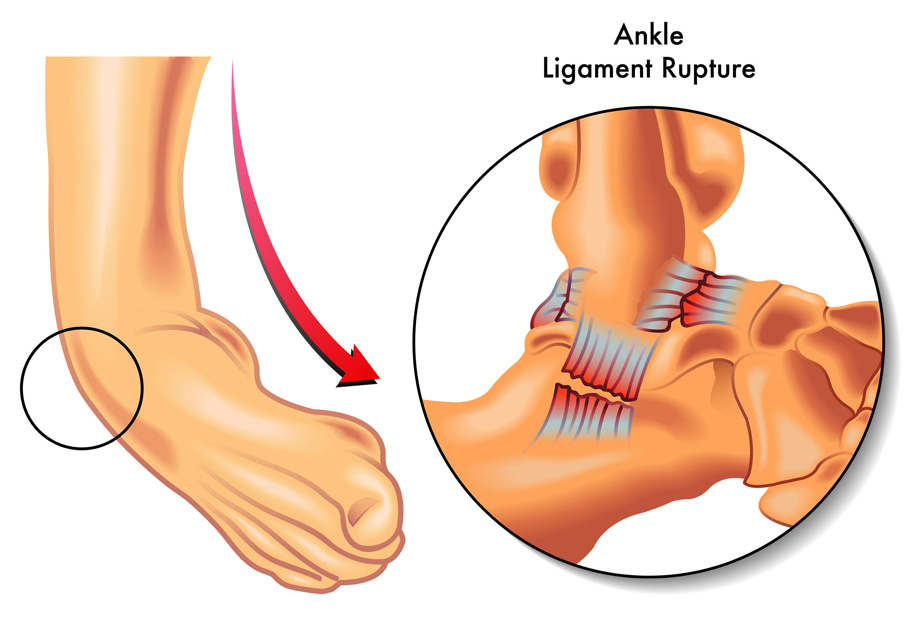
Ankle Sprains
- What is Ankle Sprain:
- An ankle sprain occurs when the ligaments that support the ankle stretch or tear, commonly happening during activities that involve sudden twists or impacts.
- Causes:
- Twisting or rolling of the ankle during physical activities.
- Awkward landings or missteps.
- Forceful impacts or collisions.
- Walking or exercising on uneven surfaces.
- Symptoms:
- Immediate pain and tenderness around the ankle.
- Swelling and bruising.
- Difficulty bearing weight on the affected ankle.
- Stiffness and limited range of motion.
- Prevention:
- Incorporate balance exercises into your routine.
- Strengthen ankle muscles through targeted exercises.
- Wear supportive footwear, especially during physical activities.
- Be cautious on uneven surfaces.
- Implement proper warm-up routines before engaging in sports or exercise.
- Treatment:
- Non-Surgical Approaches: RICE method (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) in the initial stages.
- Pain management through over-the-counter medications.
- Immobilization using braces or splints.
- Physical therapy for strengthening and flexibility.
- Surgical Intervention (for severe cases):
- Repair of torn ligaments.
- Reconstruction procedures in rare instances.
- Post-surgery, a structured rehabilitation program is crucial.
- Rehabilitation:
- Gradual reintroduction of weight-bearing activities.
- Range of motion exercises.
- Strengthening exercises for ankle stability.
- Functional exercises to restore normal movement patterns.
- Return-to-play protocols under the guidance of healthcare professionals.
Understanding the nature of ankle sprains, recognizing symptoms promptly, implementing preventive measures, and pursuing appropriate treatment options are crucial for effective management and recovery from this common lower extremity injury.
Breaststroker's Knee
- What is Breaststroker's Knee:
- Causes:
- Repetitive and forceful knee extension during breaststroke swimming.
- Overuse of the knee joint without proper technique.
- Insufficient muscle strength and flexibility around the knee.
- Symptoms:
- Persistent knee pain, often on the inner side.
- Discomfort and swelling around the knee joint.
- Limited range of motion during knee flexion and extension.
- Prevention:
- Refine breaststroke swimming technique to minimize strain on the knees.
- Incorporate knee-strengthening exercises into training routines.
- Ensure proper warm-up before engaging in swimming sessions.
- Address muscle imbalances that may contribute to the condition.
- Treatment:
- Non-Surgical Approaches:Rest and modification of swimming activities to avoid exacerbation.
- Application of ice to reduce inflammation.
- Anti-inflammatory medications for pain management.
- Physical therapy focusing on strengthening and flexibility.
Breaststroker's Knee refers to a condition where swimmers, particularly breaststroke swimmers, experience knee pain due to repetitive knee movements involved in the stroke.
- Surgical Intervention (for severe cases):
- Rarely required, and usually involves addressing underlying issues.
- Surgical procedures may include repairing damaged structures.
- Rehabilitation:
- Gradual return to swimming with modified techniques.
- Specific exercises to strengthen the muscles supporting the knee.
- Stretching routines to enhance flexibility.
- Monitoring for any signs of recurrence or worsening symptoms.
- Collaboration with healthcare professionals for a tailored recovery plan.
- Understanding Breaststroker's Knee, recognizing symptoms promptly, implementing preventive measures, and pursuing appropriate treatment options are crucial for swimmers to manage this condition effectively and resume their sport with minimized risk of recurrence.
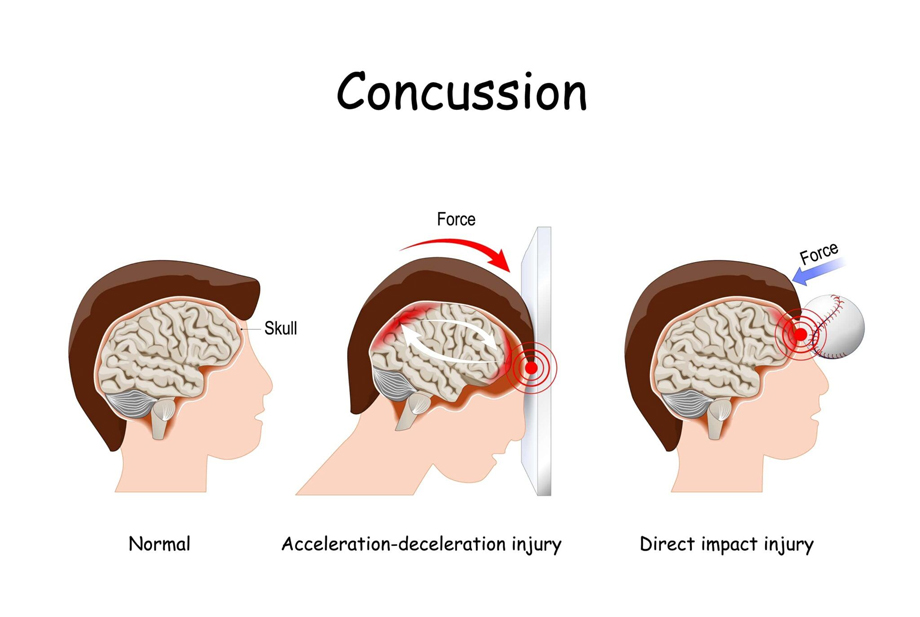
Concussions
- What is a Concussion:
- Causes:
- Head impact during sports activities (e.g., collisions, falls).
- Motor vehicle accidents.
- Physical altercations or falls.
- Symptoms:
- Headache and pressure in the head.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Confusion and memory loss.
- Dizziness and difficulty maintaining balance.
- Sensitivity to light and sound.
- Prevention:
- Use of appropriate protective gear in contact sports.
- Adherence to safety rules and regulations.
- Proper technique training in sports with a risk of head injuries.
- Regular health check-ups to address underlying conditions.
- Treatment:
- Immediate Steps:Removal from the activity causing the concussion.
- Physical and cognitive rest.
- Medical Supervision:
- Evaluation by healthcare professionals.
- Cognitive rest, limiting activities that strain the brain.
- Medication for symptom management (under medical guidance).
A concussion is a traumatic brain injury resulting from a blow, jolt, or impact to the head or body, causing the brain to move rapidly within the skull.
- Gradual Return to Activity:
- Follow a stepwise return-to-play protocol.
- Clearance from medical professionals before resuming full activity.
- Rehabilitation:
- Gradual reintegration into daily activities.
- Cognitive rehabilitation for memory and concentration.
- Monitoring for any lingering symptoms.
- Education on concussion prevention and recognition.
- Understanding the nature of concussions, prompt recognition of symptoms, adherence to preventive measures, and appropriate medical intervention are crucial for managing this type of traumatic brain injury and ensuring a safe return to activities.
Dislocated Shoulders
- What is a Dislocated Shoulder:
- Causes:
- Forceful impact or trauma to the shoulder.
- Extreme rotation of the arm.
- Falls or accidents, especially with outstretched arms.
- Symptoms:
- Intense pain and swelling in the shoulder.
- Visible deformity or protrusion of the shoulder joint.
- Limited range of motion.
- Tingling or numbness in the affected arm.
- Prevention:
- Strengthening exercises to enhance shoulder stability.
- Avoiding risky activities that may lead to falls or impacts.
- Proper warm-up before engaging in physical activities.
- Use of protective gear, especially in contact sports.
- Treatment:
- Immediate Care:Avoid attempts to self-relocate the shoulder.
- Immobilize the arm with a sling or cloth.
- Medical Intervention:
- Professional relocation of the dislocated shoulder.
- Pain management through medication.
- X-rays or imaging to assess damage.
A dislocated shoulder occurs when the upper arm bone (humerus) pops out of the shoulder socket, disrupting normal joint function.
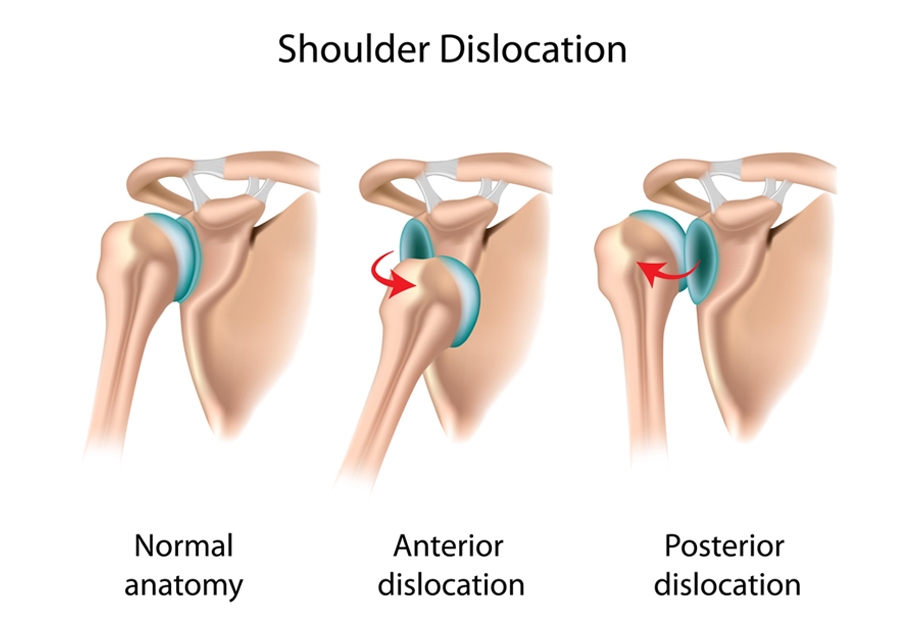
- Rehabilitation:
- Physical therapy to restore range of motion and strength.
- Gradual reintroduction of shoulder exercises.
- Strengthening of surrounding muscles for added stability.
- Preventive Measures Post-Dislocation:
- Modification of activities to prevent recurrence.
- Consultation with a healthcare professional for ongoing care.
- Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms promptly, implementing preventive measures, and pursuing appropriate treatment options are essential for managing dislocated shoulders and promoting a full recovery with reduced risk of recurrence.
Finger Dislocations/Fractures.
- What are Finger Dislocations/Fractures:
- Causes:
- Impact or bending of the fingers during accidents or sports.
- Crushing injuries or direct blows to the hand.
- Forceful twisting or hyperextension of the fingers.
- Symptoms:
- Swelling, pain, and immediate deformity of the affected finger.
- Difficulty in moving the finger or maintaining a grip.
- Visible misalignment or abnormal positioning of the finger.
- Prevention:
- Use of protective gear, such as gloves, during sports or activities.
- Awareness of hand safety in workplaces with potential hand injuries.
- Adequate warm-up routines before engaging in physical activities.
- Strengthening exercises to enhance hand and finger strength.
- Treatment:
- Immediate Care:Immobilization of the affected finger using a splint.
- Application of ice to reduce swelling.
- Avoiding any attempts to realign the dislocated finger.
- Medical Intervention:
- Professional assessment to determine the extent of the injury.
- X-rays or imaging for a detailed view of fractures or dislocations.
- Manipulation or reduction for dislocations.
- Splinting or casting for fractures.
Finger dislocations involve the displacement of bones at the joint, while fractures refer to the breakage of the finger bones. Both conditions result from trauma or forceful impact to the hand.
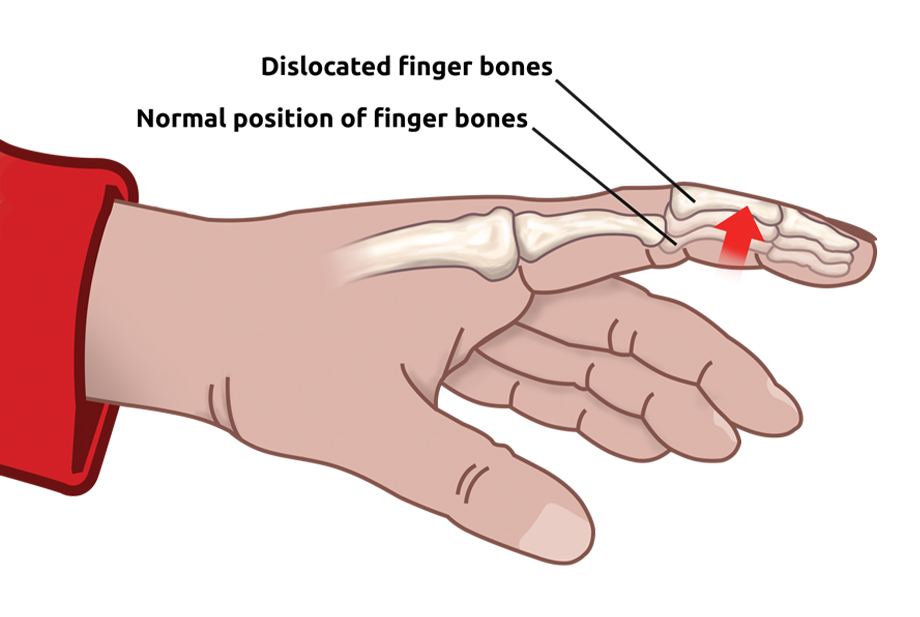
- Rehabilitation:
- Physical therapy to restore finger mobility and strength.
- Gradual reintroduction of hand and finger exercises.
- Monitoring for any signs of complications or stiffness.
- Preventive Measures Post-Injury:
- Adhering to rehabilitation exercises for full recovery.
- Modification of activities to avoid stressing the injured finger.
- Follow-up appointments with healthcare professionals for ongoing care.
- Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms promptly, implementing preventive measures, and pursuing appropriate treatment options are crucial for managing finger dislocations/fractures and facilitating a successful recovery with minimized risk of complications.
Fractures
- What is a Fracture:
- Causes:
- Direct impact or trauma to the bone.
- Falls from heights.
- Repetitive stress or overuse injuries.
- Medical conditions weakening bones (e.g., osteoporosis).
- Symptoms:
- Intense pain at the fracture site.
- Swelling and bruising.
- Visible deformity or misalignment.
- Difficulty or inability to move the affected limb.
- Prevention:
- Safety measures to prevent falls or accidents.
- Use of protective gear during sports and physical activities.
- Adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D for bone health.
- Regular exercise to strengthen bones and muscles.
- Treatment:
- Immediate Care:Immobilization of the affected limb to prevent further injury.
- Application of ice to reduce swelling.
- Avoiding any attempts to realign the dislocated finger.
- Elevation to minimize swelling.
- Medical Intervention:
- X-rays or imaging to diagnose the type and extent of the fracture.
- Reduction or realignment of displaced bones.
- Casting, splinting, or bracing for stabilization.
- Surgery for complex fractures, involving internal fixation or external devices.
A fracture is a break or crack in a bone, often resulting from excessive force, trauma, or stress.
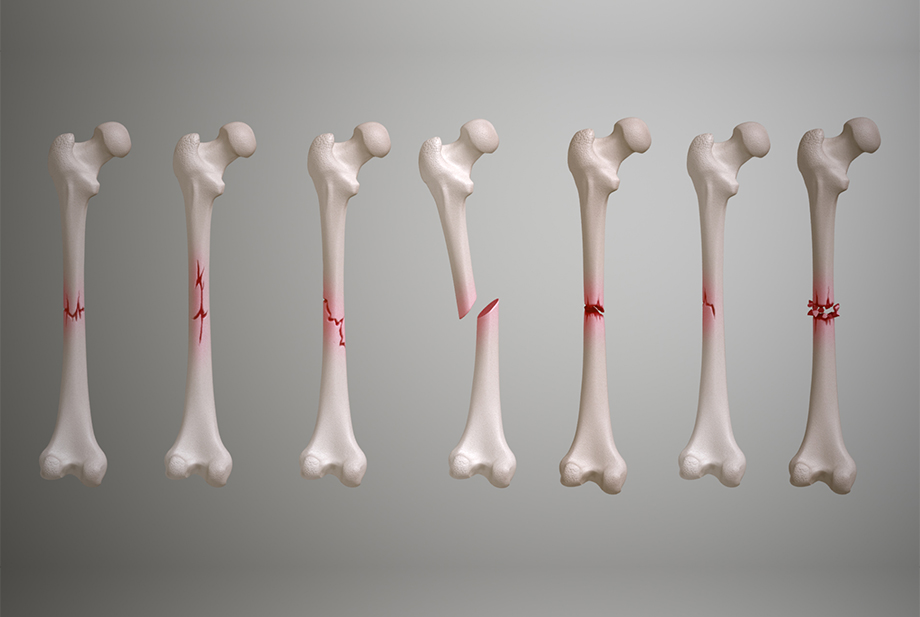
- Rehabilitation:
- Physical therapy to restore range of motion and strength.
- Gradual weight-bearing exercises as advised by healthcare professionals.
- Monitoring for any signs of complications or stiffness.
- Monitoring for signs of complications, such as infection or delayed healing.
- Preventive Measures Post-Fracture:
- Adherence to rehabilitation exercises for optimal recovery.
- Modification of activities to avoid stressing the healed bone.
- Follow-up appointments with healthcare professionals for ongoing evaluation.
- Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms promptly, implementing preventive measures, and pursuing appropriate treatment options are crucial for managing fractures and promoting a successful recovery with reduced risk of complications.
Hamstring Strain
- What is Hamstring Strain:
- Causes:
- Sudden and forceful contraction of the hamstring muscles.
- Overexertion or pushing beyond the muscle's capacity.
- Improper warm-up before intense physical activity.
- Previous hamstring injuries increasing susceptibility.
- Symptoms:
- Sudden, sharp pain in the back of the thigh.
- Swelling and tenderness.
- Difficulty in straightening the leg or standing.
- Bruising in severe cases.
- Prevention:
- Adequate warm-up with dynamic stretching before exercise.
- Gradual progression in intensity and duration of physical activity.
- Regular strengthening exercises for the hamstring muscles.
- Proper hydration to prevent muscle cramps.
- Treatment:
- Immediate Care:Rest and avoid further strain on the affected leg
- Application of ice to reduce swelling
- Compression using a bandage.
- Elevation to minimize swellin
- Medical Intervention:
- Professional assessment to determine the severity of the strain.
- Physical therapy for muscle strengthening and flexibility.
- Use of anti-inflammatory medications for pain management.
A hamstring strain is an injury involving the tearing or stretching of the muscles or tendons at the back of the thigh.
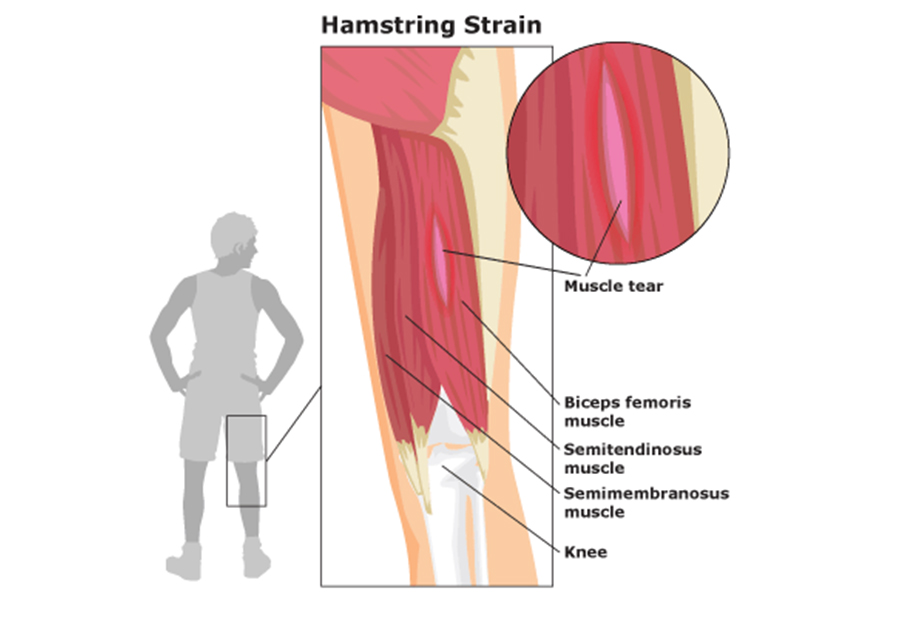
- Rehabilitation:
- Gradual reintroduction of stretching and strengthening exercises.
- Progressive return to physical activities under supervision.
- Monitoring for signs of recurrence or persistent weakness.
- Preventive Measures Post-Fracture:
- Implementation of ongoing stretching and strengthening routines.
- Modification of exercise techniques to avoid strain on the hamstrings.
- Awareness of individual limitations and adjustments in activity levels.
- Consultation with healthcare professionals for continued guidance.
- Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms promptly, implementing preventive measures, and pursuing appropriate treatment options are essential for managing hamstring strains and facilitating a successful recovery with minimized risk of recurrence.
IT Band Syndrome
- What is IT Band Syndrome:
- Causes:
- Repetitive friction of the IT band against the lateral femoral condyle.
- Overuse or excessive strain from activities like running or cycling.
- Muscular imbalances, particularly in the hip and thigh muscles.
- Poor biomechanics, such as improper running or cycling techniques.
- Symptoms:
- Sharp or burning pain on the outside of the knee or hip.
- Swelling or thickening of the IT band near the knee.
- Pain exacerbated by activities involving knee flexion and extension.
- Tenderness along the outside of the thigh.
- Prevention:
- Gradual increase in intensity and duration of physical activities.
- Incorporation of cross-training to reduce repetitive stress on the IT band.
- Proper warm-up and cool-down routines before and after exercise.
- Strengthening exercises for hip abductors and gluteal muscles.
- Treatment:
- Immediate Care:Rest and avoidance of activities causing IT band pain.
- Application of ice to reduce inflammation.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Medical Intervention:
- Professional assessment through physical examination.
- Prescription of anti-inflammatories or pain medications.
- Physical therapy for targeted stretching and strengthening exercises.
- Evaluation and correction of biomechanical factors.
IT Band Syndrome, or iliotibial band syndrome, is a common overuse injury that involves irritation and inflammation of the iliotibial band, a thick band of tissue running along the outside of the thigh.
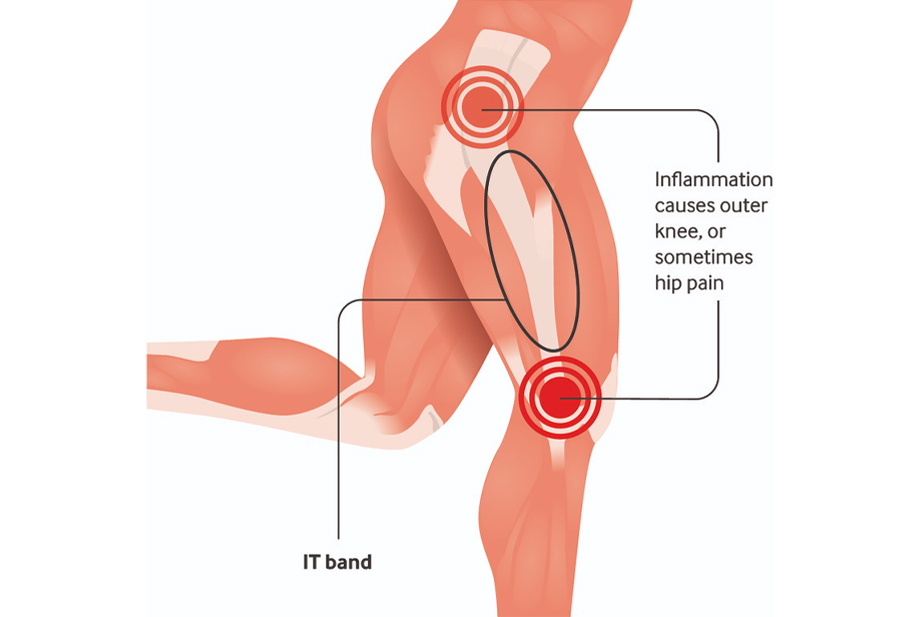
- Rehabilitation:
- Gradual reintroduction of activities, focusing on proper form.
- Stretching exercises to improve flexibility of the IT band.
- Strengthening exercises for hip muscles.
- Modification of training techniques to prevent recurrence.
- Preventive Measures Post-Treatment:
- Continued practice of stretching and strengthening exercises.
- Monitoring for signs of IT band discomfort during activities.
- Use of proper footwear and equipment during exercise.
- Consultation with healthcare professionals for ongoing guidance.
- Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms promptly, implementing preventive measures, and pursuing appropriate treatment options are crucial for managing IT Band Syndrome and promoting a successful recovery with minimized risk of recurrence
Knee Injuries
- What are Knee Injuries:
- Causes:
- Sudden impact or trauma, such as falls or collisions.
- Repetitive stress on the knee joint during sports or physical activities.
- Degenerative conditions like osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis.
- Overextension or hyperflexion leading to ligament tears.
- Symptoms:
- Pain, swelling, and tenderness in the knee.
- Instability or a feeling of the knee giving way.
- Difficulty in bearing weight or fully extending/flexing the knee.
- Audible popping or cracking sounds during movement.
- Prevention:
- Proper warm-up and stretching before engaging in physical activities.
- Strengthening exercises for the muscles supporting the knee.
- Use of protective gear and proper footwear during sports.
- Modification of activities to avoid excessive stress on the knee.
- Treatment:
- Immediate Care:Rest and avoidance of activities causing knee pain
- Application of ice to reduce swelling.
- Compression with a bandage for support
- Elevation to minimize inflammation
- Medical Intervention:
- Professional assessment through physical examination and imaging.
- Prescription of pain medications or anti-inflammatories.
- Physical therapy for strengthening and flexibility.
- Surgical options for severe ligament tears or cartilage damage.
Knee injuries encompass a range of conditions affecting the knee joint, including ligament tears, cartilage injuries, and strains, often resulting from various causes such as trauma, overuse, or degeneration.
- Rehabilitation:
- Gradual reintroduction of knee-strengthening exercises.
- Range-of-motion exercises to improve flexibility.
- Proprioceptive training for balance and coordination.
- Post-surgery, adherence to rehabilitation protocols.
- Preventive Measures Post-Treatment:
- Continued practice of knee-strengthening exercises.
- Modification of exercise routines based on individual limitations.
- Awareness of early signs of knee discomfort and prompt action.
- Regular follow-ups with healthcare professionals for ongoing knee health.
- Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms promptly, implementing preventive measures, and pursuing appropriate treatment options are crucial for managing knee injuries and promoting a successful recovery with minimized risk of recurrence.
Knee Strains
- What are Knee Strains:
- Causes:
- Sudden or excessive force on the knee during physical activities.
- Overuse or repetitive stress on the knee muscles.
- Incorrect landing after a jump or sudden change in direction.
- Weakness or imbalance in the muscles supporting the knee.
- Symptoms:
- Pain or tenderness around the knee joint.
- Swelling and inflammation in the affected area.
- Difficulty in fully extending or flexing the knee.
- Possible bruising or discoloration.
- Prevention:
- Proper warm-up before engaging in physical activities.
- Gradual progression in the intensity and duration of exercises.
- Strengthening exercises for the muscles around the knee.
- Use of appropriate footwear and protective gear.
- Treatment:
- Immediate Care:Rest and avoidance of activities causing knee pain.
- Application of ice to reduce swelling.
- Compression with a bandage for support.
- Elevation to minimize inflammation.
- Medical Intervention:
- Professional assessment through physical examination and imaging.
- Prescription of pain medications or anti-inflammatories.
- Physical therapy for strengthening and flexibility.
- Surgical options for severe ligament tears or cartilage damage.
Knee strains involve the stretching or tearing of the muscles or tendons around the knee joint, resulting in pain, swelling, and potential limitation of movement.
- Rehabilitation:
- Gradual reintroduction of knee-strengthening exercises.
- Range-of-motion exercises to improve flexibility.
- Proprioceptive training for balance and coordination.
- Monitoring for signs of persistent weakness or discomfort.
- Preventive Measures Post-Treatment:
- Consistent practice of knee-strengthening exercises.
- Modification of exercise routines based on individual limitations.
- Awareness of early signs of knee discomfort and prompt action.
- Consultation with healthcare professionals for ongoing knee health.
- Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms promptly, implementing preventive measures, and pursuing appropriate treatment options are crucial for managing knee strains and promoting a successful recovery with minimized risk of recurrence.
Lower Back Pain
- Lower Back Pain: Comprehensive Overview
- What is Lower Back Pain:
- Causes:
- Muscle strain due to lifting heavy objects or sudden movements.
- Herniated discs or degenerative disc disease.
- Poor posture and prolonged sitting.
- Underlying conditions like arthritis or spinal stenosis.
- Symptoms:
- Dull, aching pain in the lower back.
- Stiffness and limited range of motion.
- Pain radiating down the legs (sciatica).
- Muscle spasms or tenderness in the affected area.
- Prevention:
- Ergonomic adjustments for proper workstation setup.
- Regular breaks and neck stretches during desk work.
- Strengthening exercises for neck and shoulder muscles.
- Stress management techniques to reduce tension.
- Treatment:
- Immediate Care:Rest and avoidance of activities causing pain.
- Application of heat or cold packs to reduce inflammation.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Medical Intervention:
- Professional assessment through physical examination and imaging.
- Prescription of pain medications or muscle relaxants.
- Physical therapy for targeted exercises and stretches.
- In severe cases, surgical options may be considered.
Lower back pain refers to discomfort or pain localized in the lumbar region, often stemming from various factors affecting the muscles, ligaments, and spine.
- Rehabilitation:
- Gradual reintroduction of exercises for lower back strength.
- Posture correction and body mechanics education.
- Mind-body practices like yoga for overall well-being..
- Monitoring for signs of persistent discomfort or worsening symptoms.
- Preventive Measures Post-Treatment:
- Consistent practice of exercises for lower back health.
- Ergonomic considerations in daily activities.
- Regular check-ins with healthcare professionals for ongoing support.
- Lifestyle adjustments to promote overall spinal health.
- Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms promptly, implementing preventive measures, and pursuing appropriate treatment options are crucial for managing lower back pain and promoting a successful recovery with minimized risk of recurrence.
Neck and Shoulder Pain
- What is Neck and Shoulder Pain:
- Causes:
- Poor posture, especially during prolonged sitting or computer use.
- Muscle strain due to overuse or excessive lifting.
- Pinched nerves or herniated discs in the cervical spine.
- Underlying conditions like arthritis or degenerative disc disease.
- Symptoms:
- Aching or sharp pain in the neck and shoulders.
- Stiffness or limited range of motion.
- Headaches originating from the neck.
- Numbness or tingling in the arms or hands.
- Prevention:
- Ergonomic adjustments for proper workstation setup.
- Regular breaks and neck stretches during desk work.
- Strengthening exercises for neck and shoulder muscles.
- Stress management techniques to reduce tension.
- Treatment:
- Immediate Care:Rest and avoidance of activities causing pain.
- Application of heat or cold packs to reduce inflammation.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Medical Intervention:
- Professional assessment through physical examination and imaging.
- Prescription of pain medications or muscle relaxants.
- Physical therapy for targeted exercises and stretches.
- Corticosteroid injections for localized pain relief.
Neck and shoulder pain refers to discomfort or soreness in the cervical spine and shoulder region, often resulting from various factors affecting muscles, tendons, and nerves.
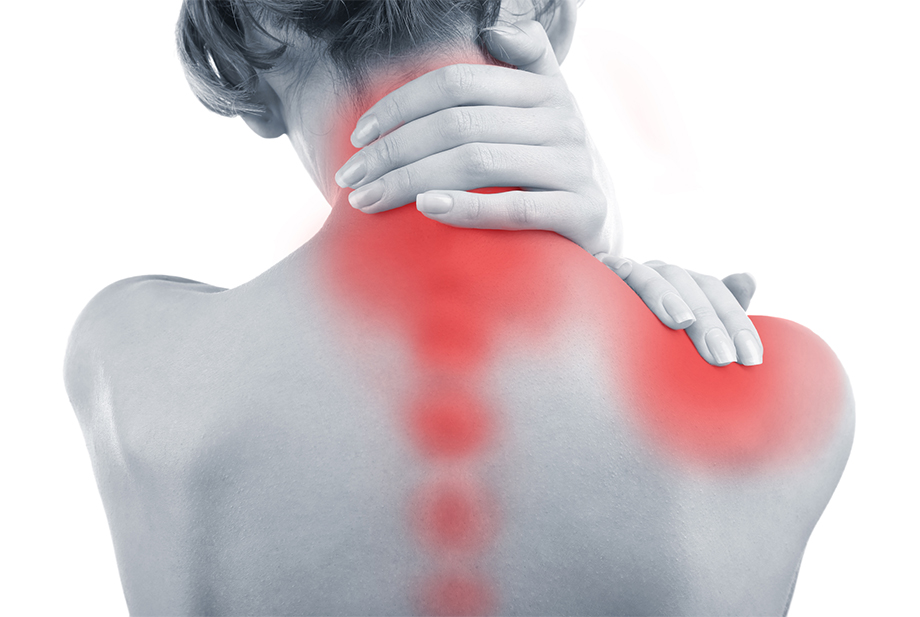
- Rehabilitation:
- Gradual reintroduction of neck and shoulder exercises.
- Posture correction and ergonomic adjustments.
- Mind-body practices like yoga for overall well-being.
- Monitoring for signs of persistent discomfort or worsening symptoms.
- Preventive Measures Post-Treatment:
- Continued practice of neck and shoulder exercises.
- Conscious effort to maintain good posture.
- Regular check-ins with healthcare professionals for ongoing support.
- Implementation of stress reduction techniques for overall health.
- Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms promptly, implementing preventive measures, and pursuing appropriate treatment options are crucial for managing neck and shoulder pain and promoting a successful recovery with minimized risk of recurrence.
Rotator Cuff Injuries
- What are Rotator Cuff Injuries:
- Causes:
- Repetitive overhead arm movements, common in sports like baseball or swimming.
- Trauma or injury, such as a fall or sudden impact.
- Degeneration due to aging, leading to wear and tear.
- Impingement, where the cuff rubs against the shoulder blade.
- Symptoms:
- Dull, persistent shoulder pain, especially during arm movements.
- Weakness and difficulty lifting or rotating the arm.
- Popping or clicking sensations in the shoulder.
- Gradual loss of shoulder strength and range of motion.
- Prevention:
- Regular shoulder-strengthening exercises.
- Proper warm-up before engaging in activities involving shoulder use.
- Technique refinement for sports with overhead arm motions.
- Adequate rest and recovery periods.
- Treatment:
- Immediate Care:Rest and avoidance of activities causing shoulder pain.
- Application of ice to reduce swelling.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Medical Intervention:
- Professional assessment through physical examination and imaging.
- Prescription of pain medications or muscle relaxants.
- Physical therapy for targeted exercises and stretches.
- Corticosteroid injections for localized pain relief.
Rotator cuff injuries encompass a range of conditions affecting the group of muscles and tendons surrounding the shoulder joint, leading to pain and impaired function.
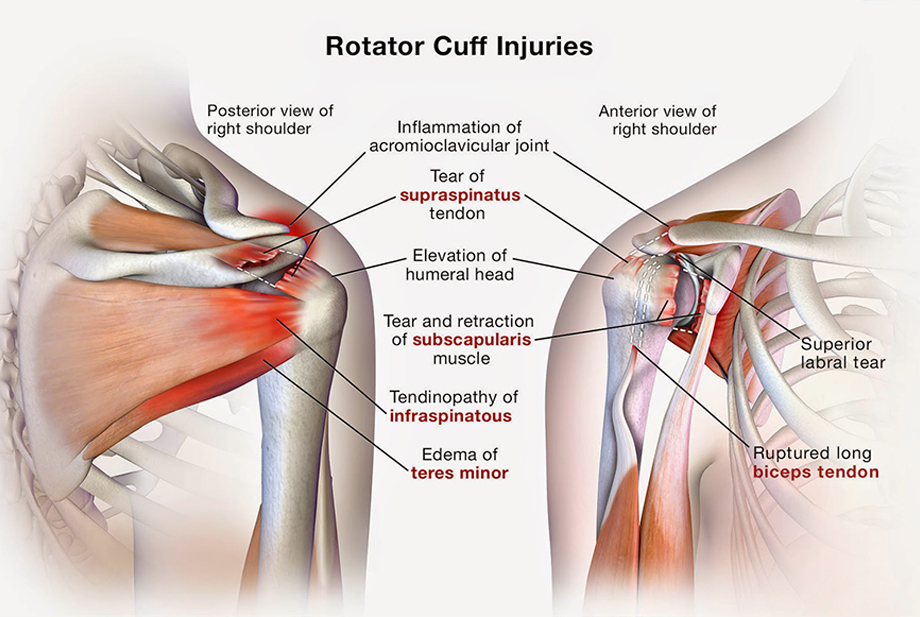
- Rehabilitation:
- Gradual reintroduction of shoulder-strengthening exercises.
- Progressive range-of-motion exercises.
- Modification of activities to avoid straining the affected shoulder.
- Monitoring for signs of persistent weakness or discomfort.
- Preventive Measures Post-Treatment:
- Continued shoulder-strengthening exercises for ongoing support.
- Modification of exercise routines based on individual limitations.
- Awareness of early signs of shoulder discomfort and prompt action.
- Consultation with healthcare professionals for ongoing shoulder health.
- Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms promptly, implementing preventive measures, and pursuing appropriate treatment options are crucial for managing rotator cuff injuries and promoting a successful recovery with minimized risk of recurrence.
Rotator Cuff Tears
- What are Rotator Cuff Tears:
- Causes:
- Repetitive overhead arm motions, common in sports like baseball or tennis.
- Trauma or injury, such as a fall onto an outstretched arm.
- Age-related wear and tear, leading to degeneration.
- Impingement, where the cuff rubs against the shoulder blade.
- Symptoms:
- Dull, aching pain in the shoulder, especially during arm movements.
- Weakness and difficulty in lifting or rotating the arm.
- Cracking or popping sensations.
- Gradual loss of shoulder strength and range of motion.
- Prevention:
- Regular shoulder-strengthening exercises.
- Proper warm-up before engaging in activities involving shoulder use.
- Technique refinement for sports involving overhead arm motions.
- Adequate rest and recovery periods.
- Treatment:
- Immediate Care:Rest and avoidance of activities causing shoulder pain.
- Application of ice to reduce swelling.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Medical Intervention:
- Professional assessment through physical examination and imaging.
- Prescription of pain medications or anti-inflammatories.
- Physical therapy for strengthening and flexibility.
- Corticosteroid injections for pain relief.
Rotator cuff tears involve the tearing of the group of muscles and tendons surrounding the shoulder joint, impairing the joint's stability and range of motion.
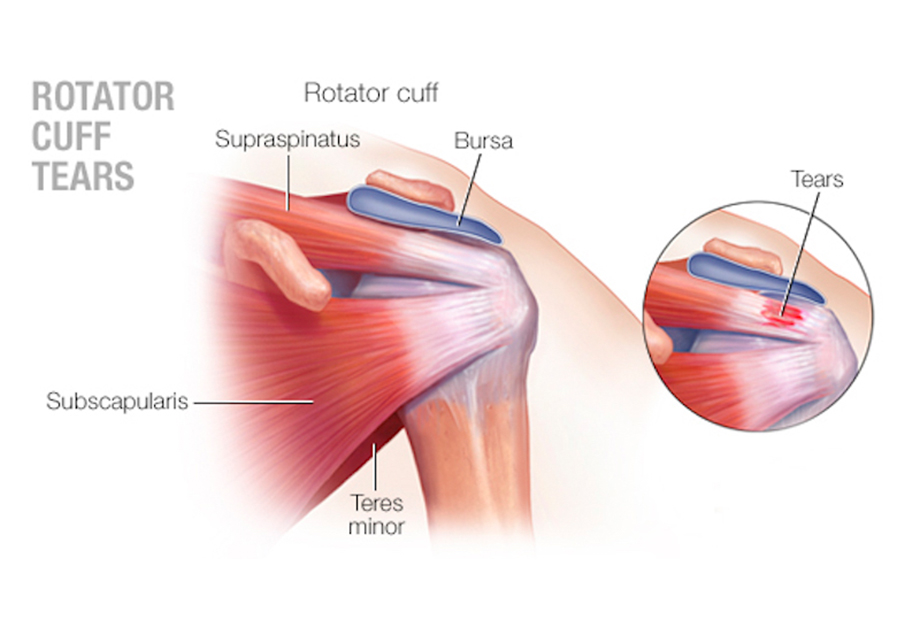
- Rehabilitation:
- Gradual reintroduction of shoulder-strengthening exercises.
- Progressive range-of-motion exercises.
- Modification of activities to avoid straining the affected shoulder.
- Monitoring for signs of persistent weakness or discomfort.
- Preventive Measures Post-Treatment:
- Continued shoulder-strengthening exercises for ongoing support.
- Modification of exercise routines based on individual limitations.
- Awareness of early signs of shoulder discomfort and prompt action..
- Consultation with healthcare professionals for ongoing shoulder health.
- Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms promptly, implementing preventive measures, and pursuing appropriate treatment options are crucial for managing rotator cuff tears and promoting a successful recovery with minimized risk of recurrence.
Runner's Knee
- What is Runner's Knee:
- Causes:
- Overuse or repetitive stress on the knee joint.
- Weakness or imbalance in thigh muscles.
- Misalignment of the kneecap.
- Changes in physical activity intensity or terrain.
- Symptoms:
- Dull, aching pain around or behind the kneecap.
- Pain worsens during activities like running, climbing, or descending stairs.
- Grinding sensation or popping noises.
- Swelling or stiffness around the knee.
- Prevention:
- Gradual increase in running intensity and distance.
- Strengthening exercises for quadriceps and hamstrings.
- Proper footwear with good shock absorption.
- Warm-up and stretching routines before running.
- Treatment:
- Immediate Care:Rest and avoidance of activities causing pain.
- Application of ice to reduce swelling.
- Compression with a bandage.
- Elevation to minimize inflammation.
- Medical Intervention:
- Professional assessment through physical examination and imaging.
- Prescription of pain medications or anti-inflammatories.
- Physical therapy for strengthening and flexibility.
- Utilization of knee braces for support.
Runner's knee, or patellofemoral pain syndrome, is a common condition characterized by pain around or behind the kneecap, often aggravated by activities like running or jumping.

- Rehabilitation:
- Gradual reintroduction of running or high-impact activities.
- Specific exercises to address muscle imbalances.
- Modification of running techniques to reduce impact.
- Monitoring for signs of persistent discomfort.
- Preventive Measures Post-Treatment:
- Consistent use of proper footwear during running activities.
- Regular stretching and strengthening exercises for knee support.
- Listening to the body's signals and taking breaks when needed.
- Consultation with healthcare professionals for ongoing guidance.
- Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms promptly, implementing preventive measures, and pursuing appropriate treatment options are crucial for managing runner's knee and promoting a successful recovery with minimized risk of recurrence.
Saddle Sores
- What are Saddle Sores:
- Causes:
- Friction and pressure from prolonged cycling.
- Incorrect saddle height or position.
- Poorly fitting cycling shorts.
- Excessive moisture and lack of ventilation.
- Symptoms:
- Redness, inflammation, or raised bumps in the perineal region.
- Pain or tenderness while sitting or cycling.
- Development of pustules or open sores.
- Itching or discomfort in the affected area.
- Prevention:
- Proper bike setup with correct saddle height and alignment.
- Use of well-fitted, moisture-wicking cycling shorts.
- Regular application of chamois cream for lubrication.
- Taking breaks during long rides to relieve pressure.
- Treatment:
- Immediate Care:Cleansing the affected area with mild soap and water.
- Application of over-the-counter antibiotic ointment.
- Wearing loose-fitting clothing to reduce friction.
- Medical Intervention:
- Professional examination for severe or persistent sores.
- Prescription of topical antibiotics or corticosteroids.
- Adjustment of bike setup or saddle for prevention.
Saddle sores are skin irritations or lesions that develop in the perineal area due to prolonged and repetitive friction between the bicycle saddle and the skin.

- Rehabilitation:
- Temporary avoidance of cycling to allow healing.
- Gradual return to cycling with proper preventive measures.
- Use of protective padding or cushions on the saddle.
- Monitoring for signs of recurrent irritation.
- Preventive Measures Post-Treatment:
- Regular inspection of the perineal area for any signs of irritation.
- Consistent use of appropriate cycling gear and chamois cream.
- Listening to the body's signals and taking breaks during long rides.
- Consultation with healthcare professionals for ongoing advice.
- Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms promptly, implementing preventive measures, and pursuing appropriate treatment options are crucial for managing saddle sores and promoting a successful recovery with minimized risk of recurrence.
Shin Splints
- What are Shin Splints:
- Causes:
- Friction and pressure from prolonged cycling.
- Incorrect saddle height or position.
- Poorly fitting cycling shorts.
- Excessive moisture and lack of ventilation.
- Symptoms:
- Redness, inflammation, or raised bumps in the perineal region.
- Pain or tenderness while sitting or cycling.
- Development of pustules or open sores.
- Itching or discomfort in the affected area.
- Prevention:
- Proper bike setup with correct saddle height and alignment.
- Use of well-fitted, moisture-wicking cycling shorts.
- Regular application of chamois cream for lubrication.
- Taking breaks during long rides to relieve pressure.
- Treatment:
- Immediate Care:Cleansing the affected area with mild soap and water.
- Application of over-the-counter antibiotic ointment.
- Wearing loose-fitting clothing to reduce friction.
- Medical Intervention:
- Professional examination for severe or persistent sores.
- Prescription of topical antibiotics or corticosteroids.
- Adjustment of bike setup or saddle for prevention.
Shin splints, or medial tibial stress syndrome, refer to pain along the shinbone (tibia) caused by excessive stress on the leg muscles and connective tissues.
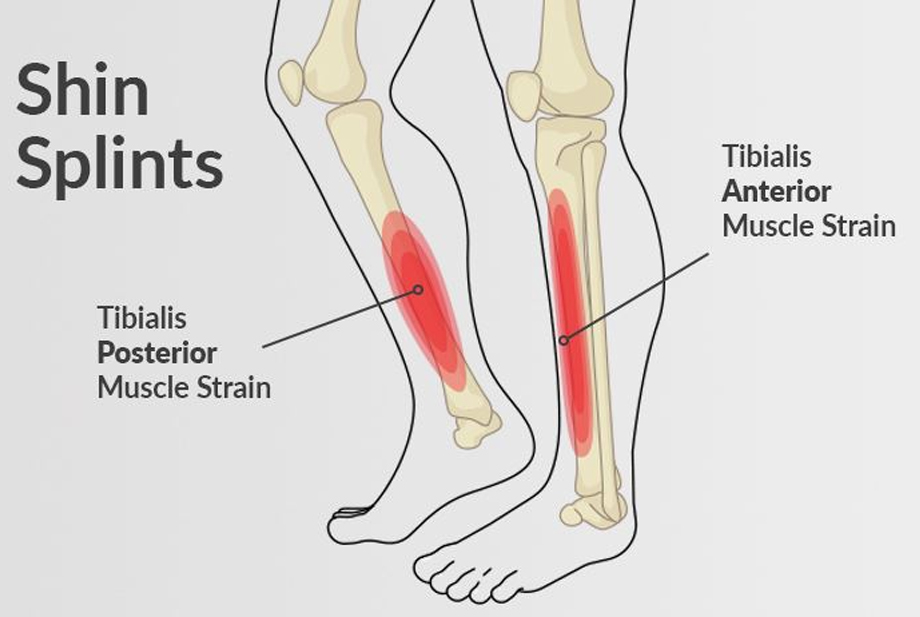
- Rehabilitation:
- Temporary avoidance of cycling to allow healing.
- Gradual return to cycling with proper preventive measures.
- Use of protective padding or cushions on the saddle.
- Monitoring for signs of recurrent irritation.
- Preventive Measures Post-Treatment:
- Regular inspection of the perineal area for any signs of irritation.
- Consistent use of appropriate cycling gear and chamois cream.
- Listening to the body's signals and taking breaks during long rides.
- Consultation with healthcare professionals for ongoing advice.
- Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms promptly, implementing preventive measures, and pursuing appropriate treatment options are crucial for managing saddle sores and promoting a successful recovery with minimized risk of recurrence.
Stress Fractures
- What are Stress Fractures:
- Causes:
- Repetitive high-impact activities, such as running or jumping.
- Insufficient rest between intense physical activities.
- Changes in training surfaces or footwear.
- Conditions that weaken bones, like osteoporosis.
- Symptoms:
- Gradual onset of localized pain during physical activity.
- Pain that diminishes with rest but returns upon activity.
- Swelling and tenderness at the site of the fracture.
- Possible bruising over the affected area.
- Prevention:
- Gradual progression in the intensity and duration of physical activities.
- Adequate rest periods between high-impact sessions.
- Wearing appropriate footwear for specific activities.
- Incorporating low-impact exercises to reduce stress on bones.
- Treatment:
- Immediate Care:Rest and avoidance of activities causing pain.
- Application of ice to reduce swelling.
- Elevation to minimize inflammation.
- Medical Intervention:
- Professional assessment through imaging (X-rays, MRI).
- Prescription of pain-relieving medications.
- Utilization of walking aids, such as crutches, to avoid weight-bearing.
- Customized rehabilitation plans, including physical therapy.
Stress fractures are small cracks or fractures in bones, typically caused by repetitive stress, overuse, or prolonged impact on a particular area.
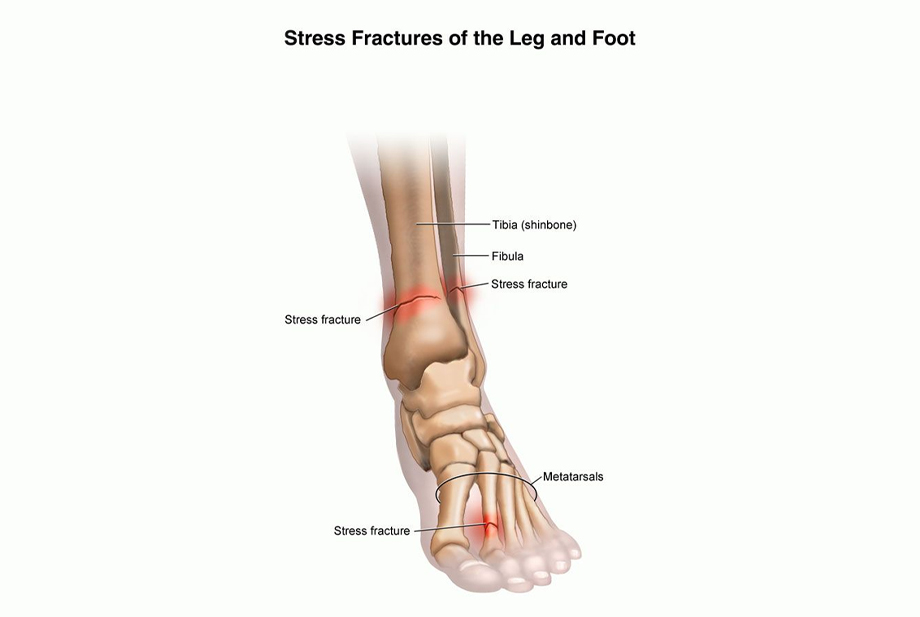
- Rehabilitation:
- Gradual reintroduction of weight-bearing activities.
- Specific exercises to improve bone density and strength.
- Monitoring for signs of persistent pain or complications.
- Adjustment of training techniques to prevent recurrence.
- Preventive Measures Post-Treatment:
- Regular bone density assessments, especially for at-risk individuals.
- Modification of exercise routines based on individual limitations.
- Adherence to prescribed rehabilitation exercises for ongoing bone health.
- Consultation with healthcare professionals for continued guidance.
- Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms promptly, implementing preventive measures, and pursuing appropriate treatment options are crucial for managing stress fractures and facilitating a successful recovery with minimized risk of recurrence.
Swimmer's Ear
- What is Swimmer's Ear:
- Causes:
- Prolonged exposure to moisture in the ear canal.
- Contaminated water entering the ear during swimming.
- Scratches or abrasions in the ear canal.
- Use of objects like cotton swabs, leading to irritation.
- Symptoms:
- Itching or discomfort in the ear.
- Redness and swelling of the ear canal.
- Pain, particularly when touching or pulling the earlobe.
- Drainage of clear, odorless fluid.
- Prevention:
- Keeping ears dry by using earplugs while swimming.
- Tilting the head to allow water to drain after swimming.
- Drying ears thoroughly with a towel after water exposure.
- Avoiding the use of foreign objects in the ear canal.
- Treatment:
- Immediate Care:Avoidance of further water exposure to the affected ear.
- Application of over-the-counter ear drops for pain relief.
- Keeping the ear dry during the healing process.
- Medical Intervention:
- Professional examination to confirm the diagnosis.
- Prescription ear drops with antimicrobial properties.
- Oral antibiotics for severe infections.
- Removal of debris or excessive earwax if present.
Swimmer's ear, or otitis externa, is an infection of the outer ear canal, commonly caused by water exposure, leading to bacterial or fungal growth.
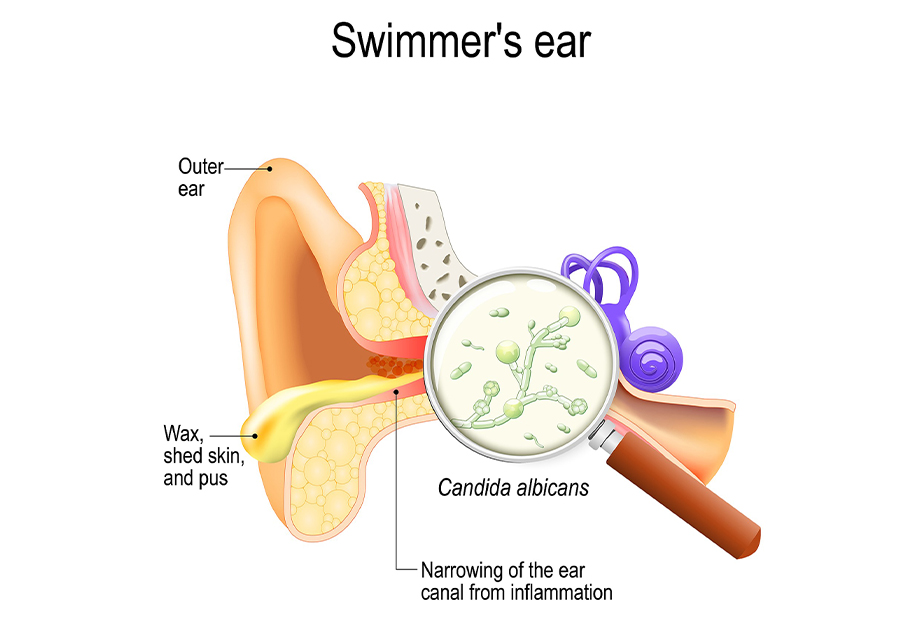
- Rehabilitation:
- Completion of the prescribed antibiotic course.
- Avoidance of swimming until the infection clears.
- Gradual reintroduction of water exposure with protective measures.
- Regular ear hygiene practices.
- Preventive Measures Post-Treatment:
- Consistent use of earplugs during water activities.
- Prompt drying of ears after any water exposure.
- Regular ear checks for signs of irritation or infection.
- Consultation with healthcare professionals for ongoing ear health.
- Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms promptly, implementing preventive measures, and pursuing appropriate treatment options are crucial for managing swimmer's ear and promoting a successful recovery with minimized risk of recurrence.
Swimmer's Shoulder
- What is Swimmer's Shoulder:
- Causes:
- Repetitive overhead arm movements during swimming.
- Inadequate warm-up or improper stretching.
- Weakness in the shoulder muscles.
- Incorrect swim stroke techniques.
- Symptoms:
- Pain in the shoulder, especially during and after swimming.
- Tenderness and swelling in the shoulder joint.
- Reduced range of motion and flexibility.
- Weakness in the affected shoulder.
- Prevention:
- Proper swim stroke technique and form.
- Gradual increase in swimming intensity and duration.
- Regular shoulder-strengthening exercises.
- Adequate warm-up and cool-down routines.
- Treatment:
- Immediate Care:Rest and avoidance of swimming until pain subsides.
- Application of ice to reduce inflammation.
- Anti-inflammatory medications for pain relief.
- Medical Intervention:
- Professional assessment to identify the root cause.
- Physical therapy to strengthen and balance shoulder muscles.
- Modification of swim techniques to reduce strain.
- Use of braces or support devices.
Swimmer's shoulder is a common term for shoulder pain experienced by swimmers, often caused by overuse, poor technique, or muscular imbalances.
- Rehabilitation:
- Gradual reintroduction of swimming, focusing on proper techniques.
- Shoulder-strengthening exercises and stretching routines.
- Monitoring for signs of persistent discomfort.
- Adjustments in swim routines based on recovery.
- Preventive Measures Post-Treatment:
- Continued shoulder-strengthening exercises for maintenance.
- Regular assessments of swim techniques for improvements.
- Listening to the body's signals and taking breaks when needed.
- Consultation with healthcare professionals for ongoing guidance.
- Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms promptly, implementing preventive measures, and pursuing appropriate treatment options are crucial for managing swimmer's shoulder and facilitating a successful recovery with minimized risk of recurrence.
Tennis Elbow
- What is Tennis Elbow:
- Causes:
- Repetitive gripping and twisting motions, common in racquet sports.
- Overuse of the forearm muscles during activities like typing or carpentry.
- Poor technique or equipment in sports activities.
- Symptoms:
- Pain and tenderness on the outer side of the elbow.
- Weakness in the grip, particularly when holding objects.
- Stiffness in the elbow joint.
- Worsening pain during gripping or lifting.
- Prevention:
- Proper technique and equipment in sports activities.
- Regular breaks during repetitive tasks involving forearm use.
- Strengthening exercises for forearm muscles.
- Use of ergonomic tools and equipment.
- Treatment:
- Immediate Care:Rest and avoidance of swimming until pain subsides.
- Application of ice to reduce inflammation.
- Anti-inflammatory medications for pain relief.
- Medical Intervention:
- Professional assessment to confirm the diagnosis.
- Physical therapy for strengthening and flexibility.
- Use of braces or splints to reduce strain.
- Anti-inflammatory medications for pain relief.
Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is a condition where the outer part of the elbow becomes painful and tender, often due to overuse of the forearm muscles and tendons.
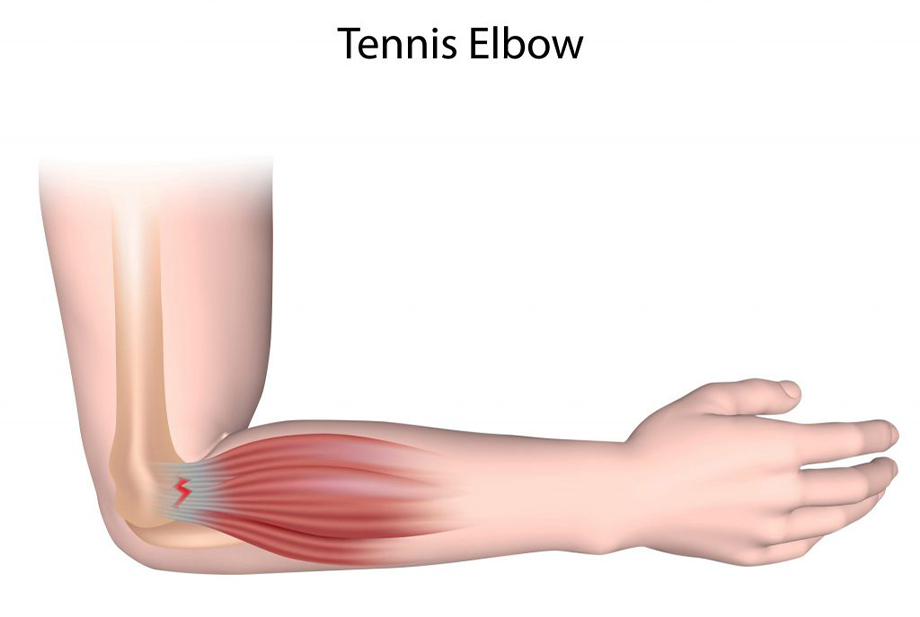
- Rehabilitation:
- Gradual reintroduction of gripping and lifting activities.
- Strengthening exercises for forearm muscles.
- Modification of techniques to prevent recurrence.
- Monitoring for signs of persistent discomfort.
- Preventive Measures Post-Treatment:
- Implementation of ergonomic practices in daily activities.
- Continued exercises to maintain forearm strength and flexibility.
- Awareness of early signs of discomfort and prompt action.
- Consultation with healthcare professionals for ongoing guidance.
- Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms promptly, implementing preventive measures, and pursuing appropriate treatment options are crucial for managing tennis elbow and facilitating a successful recovery with minimized risk of recurrence.
Get affordable and quality Sports Injury and Arthroscopy Treatment in Mumbai by Dr. Aditya Pawaskar.
To Book Appointment Call
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is a Sports Injury Specialist ?
A: A Sports Injury Specialist is a healthcare professional specializing in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of injuries related to sports and physical activities. They have expertise in assessing and managing various musculoskeletal injuries, such as sprains, strains, fractures, and dislocations, commonly occurring in athletes.
Q: How is a Sports Injury Specialist different from a general physician ?
A: While a general physician provides overall healthcare, a Sports Injury Specialist focuses specifically on injuries related to sports and physical activities. They have specialized knowledge in sports medicine, rehabilitation techniques, and sports-specific biomechanics, allowing them to tailor their treatment to athletes' unique needs.
Q: When should I consult a Sports Injury Specialist ?
A: It is advisable to consult a Sports Injury Specialist if you experience sports-related injuries such as sprains, strains, joint injuries, or if you have concerns about your athletic performance. They can provide expert diagnosis, treatment plans, and rehabilitation strategies tailored to your specific needs and goals.
Q: Can a Sports Injury Specialist help with injury prevention ?
A: Yes, Sports Injury Specialists play a crucial role in injury prevention. They can assess your biomechanics, provide guidance on proper warm-up and conditioning exercises, and offer advice on equipment and technique to reduce the risk of injuries during sports and physical activities.
Q: What services do Sports Medicine professionals offer ?
A: Sports Medicine professionals offer a range of services, including injury assessment and treatment, rehabilitation, performance enhancement, nutritional guidance, and sports psychology support. They work collaboratively to address both acute injuries and long-term health and performance goals for athletes.
Q: Q: Are Sports Medicine services only for professional athletes ?
A: No, Sports Medicine services are not exclusive to professional athletes. They are available to individuals of all ages and fitness levels who participate in sports or physical activities. Whether you're a weekend warrior, a student athlete, or someone trying to stay active, Sports Medicine professionals can provide valuable support for your health and performance.
Q: Who is Dr. Aditya Pawaskar?
A: Dr. Aditya Pawaskar is a specialist in Arthroscopy and sports injury surgery. He is a medical professional with expertise in the field of orthopedics, specifically focusing on arthroscopic procedures and the surgical management of sports-related injuries.
Q: What is Dr. Aditya Pawaskar's area of specialization?
A: Dr. Aditya Pawaskar specializes in Arthroscopy and sports injury surgery. Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that involves using a small camera to visualize and treat joint problems. In his practice, Dr. Pawaskar likely deals with a variety of orthopedic issues, particularly those related to sports injuries.
Q: What conditions or injuries does Dr. Aditya Pawaskar typically treat?
A: Dr. Aditya Pawaskar likely treats a range of conditions and injuries related to joints, with a focus on those arising from sports activities. Common issues may include ligament tears, cartilage damage, and other musculoskeletal injuries that often occur in athletes.
Q: What is the significance of arthroscopy in sports injury surgery?
A: Arthroscopy is significant in sports injury surgery as it allows for a minimally invasive approach to diagnose and treat joint problems. This technique often results in smaller incisions, less scarring, and quicker recovery times compared to traditional open surgery, making it particularly beneficial for athletes aiming for a faster return to their sport.
Q: How can one schedule a consultation with Dr. Aditya Pawaskar?
A: To schedule a consultation with Dr. Aditya Pawaskar, individuals can typically contact his medical office directly or call +91 9372832145 for appointment. Contact information are available on the www.dradityapawaskar.com website page.
Q: Does Dr. Aditya Pawaskar work with athletes of all levels or only professionals?
A: While specific details may vary, orthopedic specialists like Dr. Aditya Pawaskar often work with athletes of all levels, including amateur and recreational athletes, not just professionals. His expertise in sports injury surgery and arthroscopy likely extends to individuals with a diverse range of athletic backgrounds and activity levels.
Q: What sets Dr. Aditya Pawaskar apart in the field of Arthroscopy and sports injury surgery?
A: Dr. Aditya Pawaskar's distinction in the field of Arthroscopy and sports injury surgery may stem from his specialized training, experience, and possibly any particular innovative or advanced techniques he employs. Patient reviews, professional affiliations, and academic contributions could provide further insights into his standing